Here we archive and cross link all of the past projects done by our first year Ph.D. students, undergraduate and external guests that take part in our reading group. Generally, when students and participants outside of WING join the reading group they must also complete a related project touching on some part of the lecture topics. These projects often get presented publicly in the forum of our School of Computing’s Term Project Showcase (STePS).
Table of Contents
Volume 2025 (Semester 2510 (AY 25/26, Sem I) featured at 27th STePS, held on 12 Nov 2025)
Project 01: CompRAG: Retrieval for Multiple Hops [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Indraneel Paranjape, Nayanthara Prathap, Nura Tamton, Vangmay Sachan
Project 02: Mixture-of-LoRA-Experts for Continual Learning in Generative Retrieval [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Benjamin Chek, Choong Kai Zhe, Zak Tng
Project 03: SLM + RAG [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Jonathan Chen, Shyamal Narang, JF Koh
Project 04: Cutting Redundant Knowledge for Effective RAG [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Mingyu Lee, Swislar Tan, Ervin Teo
Project 05: ScholarAI:Simplifying Interdisciplinary AI Research Using GraphRAG [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Rishav Ghosh, Zaidan Sani, Nicholas Cheng, Qianbo Dong
Project 06: MathRAG: Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Verifying Math Solutions. [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Kseniia Petukhova, Van-Hoang Nguyen
Project 07: Fine-Grained Multimodal RAG: Enhancing Retrieval with Object-Level Representations [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Manaswini Talagadadivi, Shen Ting Ang, Huang Chao Ming, Benjamin Goh, Estelle Sim
Project 09: Automatic Accelerator Code Generation via LLM Agentic Workflow [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Takanori Aoki
Project 10: When Retrieval Misleads: Exploring Vulnerabilities in RAG [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Sahej Agarwal, Jundong Xu, Ruiwen Zhou, Sahajpreet Singh
Project 11: Contexts Ground Discourse [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Yisong Miao
Project 12: Context-Aware RAG: Enhancing Retrieval with Contextual Information [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Xinpeng Liu, Ng Xuan Hern, Oshan Jayawardena
Project 13: Improving Retrieval with Graph Pruning [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Aaron Toh, Frederick Amal Emerson, Hong Yi, Yong Ee
Project 14: A Unified Benchmark Suite for Retrieval-Augmented Speculative Decoding [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Ada Ho, Tan Chien Hao, Lee Kwan Tze, Benn Tan
Project 16: Beyond the Crowd: LLM-Augmented Community Notes for Governing Health Misinformation [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Jiaying Wu, Zihang Fu, Haonan Wang, Fanxiao Li, Min-Yen Kan
Volume 2023 (Semester 2310 (AY 23/24, Sem I) featured at 23th STePS, held on 15 Nov 2023)
Project 02: AugICL [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Xiachong Feng, Yisong Miao
Project 05: Chain of Action [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Nicholas Wong, Richmond Sin, Ellawela Suveen Thinusha Bandara, Low Keng Hoong (Warren), Gan Kah Ee
Project 06: Exploring self-supervised webscraper code generation with LLMs [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Arnav Aggarwal, Filbert Phang Kong San, Soon Kang Le (Conrad), Wee Yen Zhe, Alson Jiang
Project 09: LLM for Table Fact-Checking & Reasoning [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Naomi Leow, Xinyuan LU
Project 14: Textualization of Visual Information [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Xiao Xu
Volume 2021 (Semester 2020 (AY 20/21, Sem II) featured at 18th STePS, held on 14 Apr 2021)
Project 01: Explore Multiple Response Modalities of DialogWAE [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Liu Ruofan, Liu Hongfu, Liu Yong
Project 02: FiBiNET [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Qiao Rui, Sng Weicong, Li Zihan
Project 03: Feedback-guided Preference Adaptation Network (FPAN) [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Henry Kasim, Samuel Broughton
Project 04: Causal Estimation for Conversational Recommender Systems [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Yisong Miao, Chenxin Wang
Project 05: Counterfactual Recommender [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Aadit Rahul Kamat, Takanori Aoki
Project 06: Diversifying Dialogue Generation with Non-Conversational Text [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Yeo Qi Xun, Yuxi Xie, Tian Zhen
Project 07: Extending Neural Collaborative Filtering [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Gabriel Loye, Clarence Ong, Nham Quoc Hung, Sashankh CK
Project 08: NN for Ad Recommendation [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Muhammad Assyarul Ariffin Bin Omar, Lee Xiong An, Xu Pengtai
Project 09: Beyond IGMC [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Stephen Tan, Axel Lau Wei En, Joel Tan Wan Rong, Wendi Ren, Chan Guan Hao
Project 10: KGRecSys [ Gallery ] [ Poster ]
Evan Chong, Rabiul Awal
Projects from Semester 2510 (AY 25/26, Sem I) featured at 27th STePS, held on 12 Nov 2025.
Projects | Posters |
|---|---|
Team 01: CompRAG: Retrieval for Multiple Hops📖 AbstractCompRAG enhances multi-hop RAG by composing entity–relation-entity triplets with HRR embeddings, enabling relation-focused retrieval that bridges semantic and graph-based methods. ✍️ DescriptionCompRAG (COMPrehension and COMPosition RAG) explores how relations in a text can be expressed as composite to enhance multi-hop answering outcomes in RAG. We extract entity-relation-entity triplets from text, but innovate by leveraging Holographic Reduced Representations (HRR) [1] to compose individual triplet vectors together, preserving the direction of relations in vector embeddings. At query time, processed query vectors are matched to the most similar triplets in the index. The associated chunks form the context for the LM. By focusing retrieval on the relations present in the text rather than raw similarity or pure entity-linked graphs, CompRAG aims to bridge semantic and graph methods to improve multi-hop retrieval outcomes. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ GitHub Repository ] [ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Team 02: Mixture-of-LoRA-Experts for Continual Learning in Generative Retrieval📖 AbstractThis project implements the MixLoRA-DSI pipeline to explore continual learning in generative retrieval systems via the usage of LoRA experts. ✍️ DescriptionThis project reproduces the Mixture-of-LoRA-Experts for Generative Retrieval (MixLoRA-DSI) framework to empirically study how parameter-efficient fine-tuning enables continual learning in generative retrieval systems. We implemented the full pipeline—from T5 pretraining under RQ-based DocIDs to constrained decoding—and replicated key results on MSMARCO and NQ320k datasets. Through this process, we analyzed the interactions between LoRA modules, mixture routing, and residual quantization, identifying challenges in stability, convergence, and data handling. Our findings provide practical insights into implementing rehearsal-free generative retrievers and clarify how modular fine-tuning mechanisms can balance efficiency and plasticity in large-scale language-retrieval architectures. ☀️ Team Member📻 Media Links[ GitHub Repository ] [ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Team 03: SLM + RAG📖 AbstractThe project focuses on study of efficacy of RAG solution built on SLMs for domain specific knowledge task. ✍️ DescriptionWith the rise of Generative AI, Small Language Models (SLMs) offer a more practical and affordable solution for industrial deployment compared to Large Language Models (LLMs). For integrating domain-specific knowledge, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is often a more effective strategy than model fine-tuning. This project investigates the efficacy of RAG systems built upon SLMs. We will evaluate their performance and challenges across various question categories using product technical documents. The 2nd objective is to analyse whether the underlying language model size (SLM vs. LLM) significantly impacts the overall performance and reliability of the RAG system. ☀️ Team Member📻 Media Links[ GitHub Repository ] [ Poster ] | 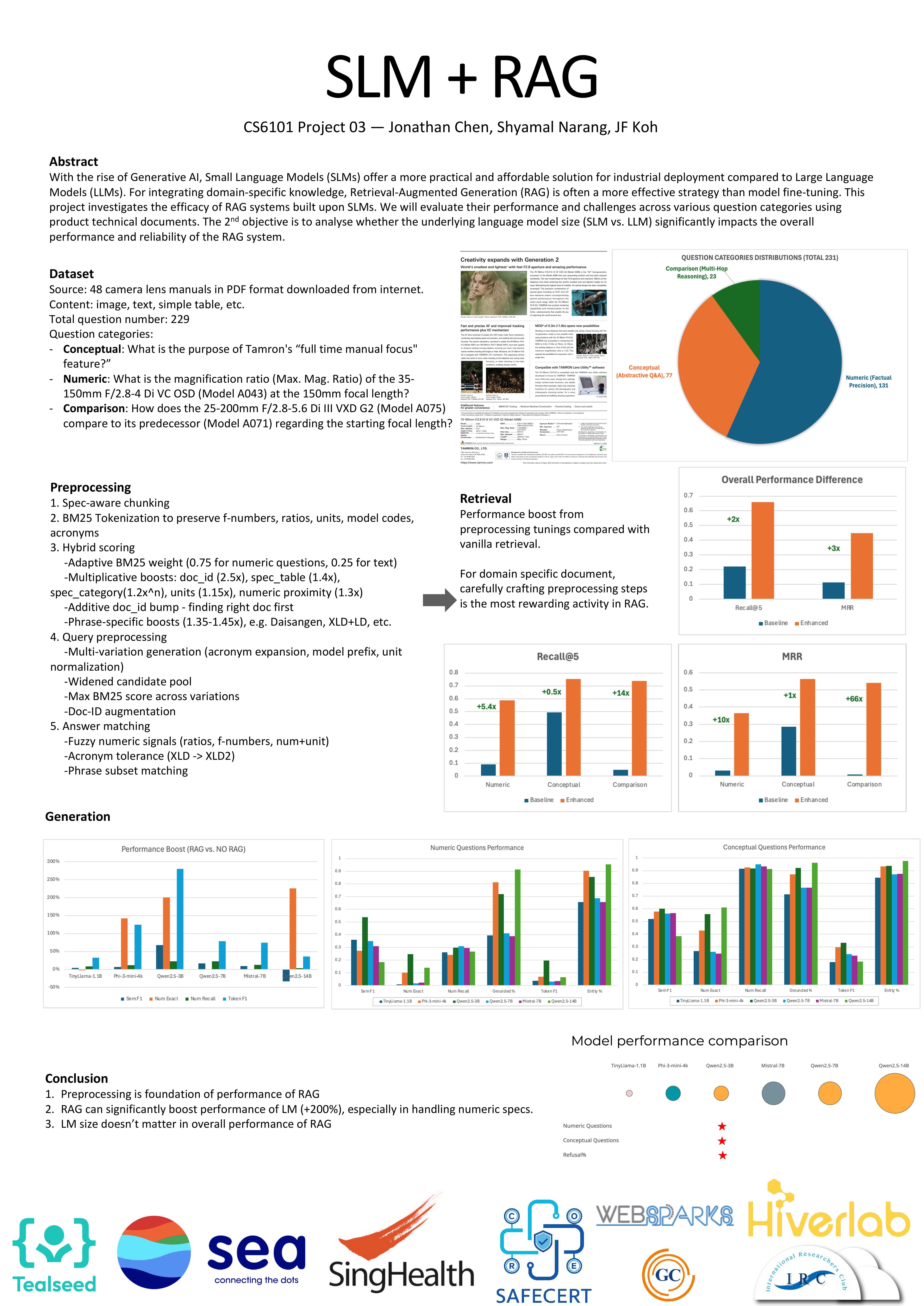 Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Team 04: Cutting Redundant Knowledge for Effective RAG📖 AbstractEvaluating the impact of corpus deduplication (SimHash, MinHash) on RAG retrieval efficiency and downstream model accuracy. ✍️ DescriptionRetrieval systems often return multiple near-duplicate documents reducing retrieval diversity and efficiency. This project addresses that challenge by clustering near-duplicates and selecting representative documents to keep Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) both efficient and relevant. We evaluate two deduplication methods on their impact on RAG performance. Overall, moderate deduplication effectively reduces redundancy without harming performance, suggesting that RAG systems can safely benefit from cleaner, more diverse corpora. ☀️ Team Member📻 Media Links[ Poster ] | 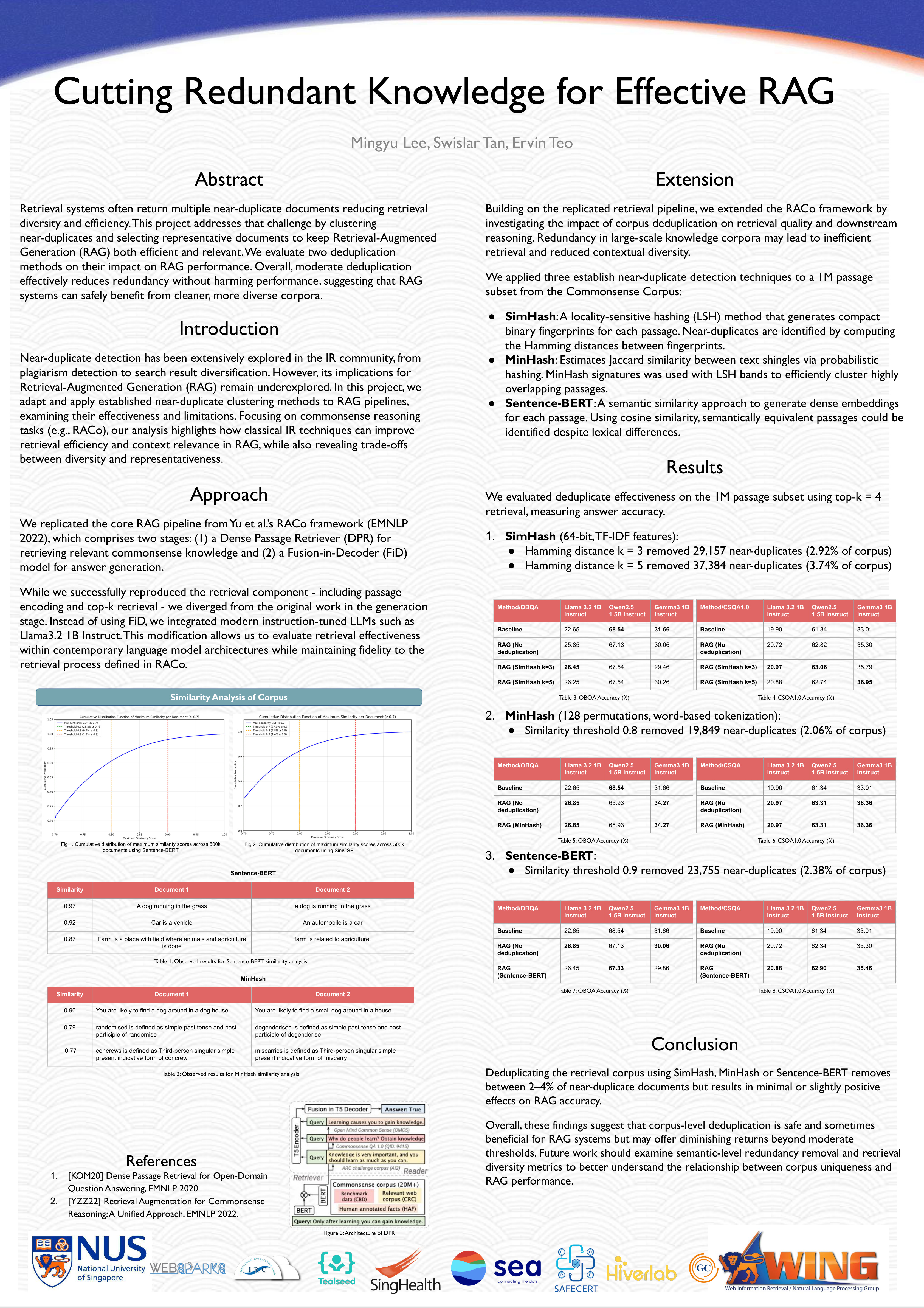 Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Team 05: ScholarAI:Simplifying Interdisciplinary AI Research Using GraphRAG📖 AbstractEnabling easier research by automated ontology extraction to generate knowledge graphs for smarter retrieval. ✍️ DescriptionThis project builds a graph- and ontology-augmented QA system over AI papers from arXiv by combining GraphRAG for entity/relation-aware retrieval with OntoRAG for schema- and rule-driven reasoning. We construct a heterogeneous knowledge graph of papers, authors, methods, datasets, align it with AI ontologies (subfields, method and dataset taxonomies), and use ontological constraints to normalize terms, resolve synonyms, and support multi-hop inference ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ GitHub Repository ] [ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Team 06: MathRAG: Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Verifying Math Solutions.📖 AbstractWe enhance step-level mathematical solution verification by augmenting LLM evaluators with external mathematical knowledge via retrieval. ✍️ DescriptionCurrent evaluations of Large Language Models (LLMs) in mathematical reasoning typically judge only the final answer and often overlook whether the intermediate steps are logically valid. Prior work on LLM-based evaluators also tends to rely solely on the model's internal parametric reasoning ability, which can be inconsistent when verifying multi-step solutions. ☀️ Team Member📻 Media Links[ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Team 07: Fine-Grained Multimodal RAG: Enhancing Retrieval with Object-Level Representations📖 AbstractThis project developed a Fine-Grained Multimodal RAG pipeline that integrates DETR object detection to enhance visual reasoning on the MRAG-Bench through structured text prompts and bounding-box overlays. ✍️ DescriptionLarge Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) struggle to effectively utilize retrieved visual knowledge for complex reasoning tasks, particularly those involving changes in perspective, scope, or occlusion, as demonstrated by the MRAG-Bench. Our llava-onevision-7b baseline model achieved a strong initial accuracy of 58.2%. We introduce an Object Detection Enhancement to the MRAG-Bench evaluation pipeline to push performance beyond the existing baseline by providing explicit visual grounding. This utilizes the DETR (DEtection TRansformer) model to analyze images and convert visual content (objects, counts, and spatial layout) into structured text descriptions. This structured analysis is used to create an Enhanced Prompt that guides the LLaVA model's reasoning. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ GitHub Repository ] [ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Team 09: Automatic Accelerator Code Generation via LLM Agentic Workflow📖 AbstractThis project explores the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) for automatic accelerator code generation and optimization. ✍️ DescriptionThe project aims to improve performance for GPU by generating CUDA C++ code, targeting algorithms commonly used for Deep Learning. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Poster ] | 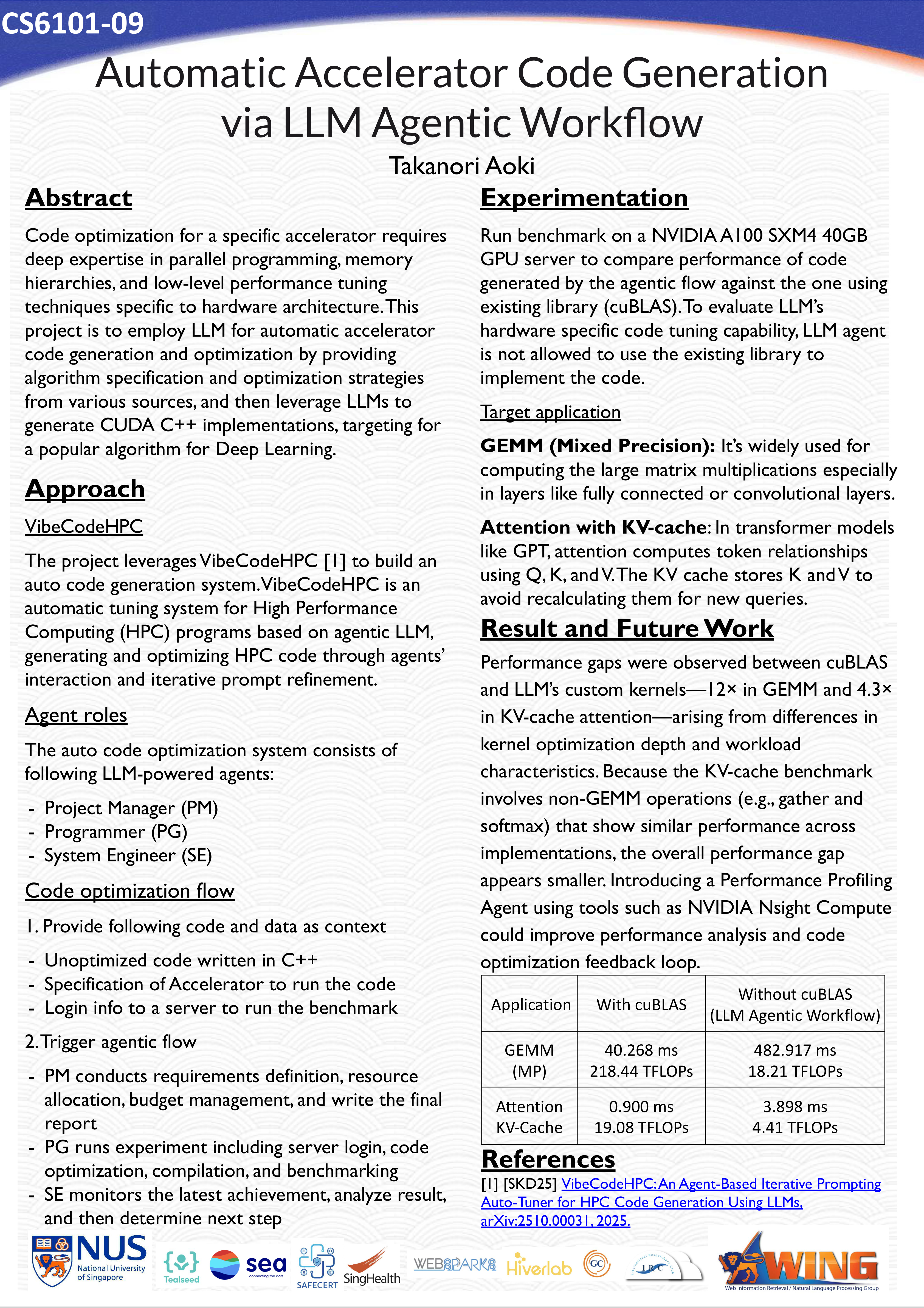 Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Team 10: When Retrieval Misleads: Exploring Vulnerabilities in RAG📖 AbstractTODO ✍️ DescriptionRetrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has succeeded in knowledge-intensive tasks as it provides LLMs with external knowledge. However, existing works show that RAG can cause increased hallucination especially when the retrieved data involves counter-intuitive information. Therefore, we aim to study how different prompting and training techniques like chain-of-thought, retrieval-augmented fine-tuning, etc. can help mitigate these issues in small size language models. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Poster ] | 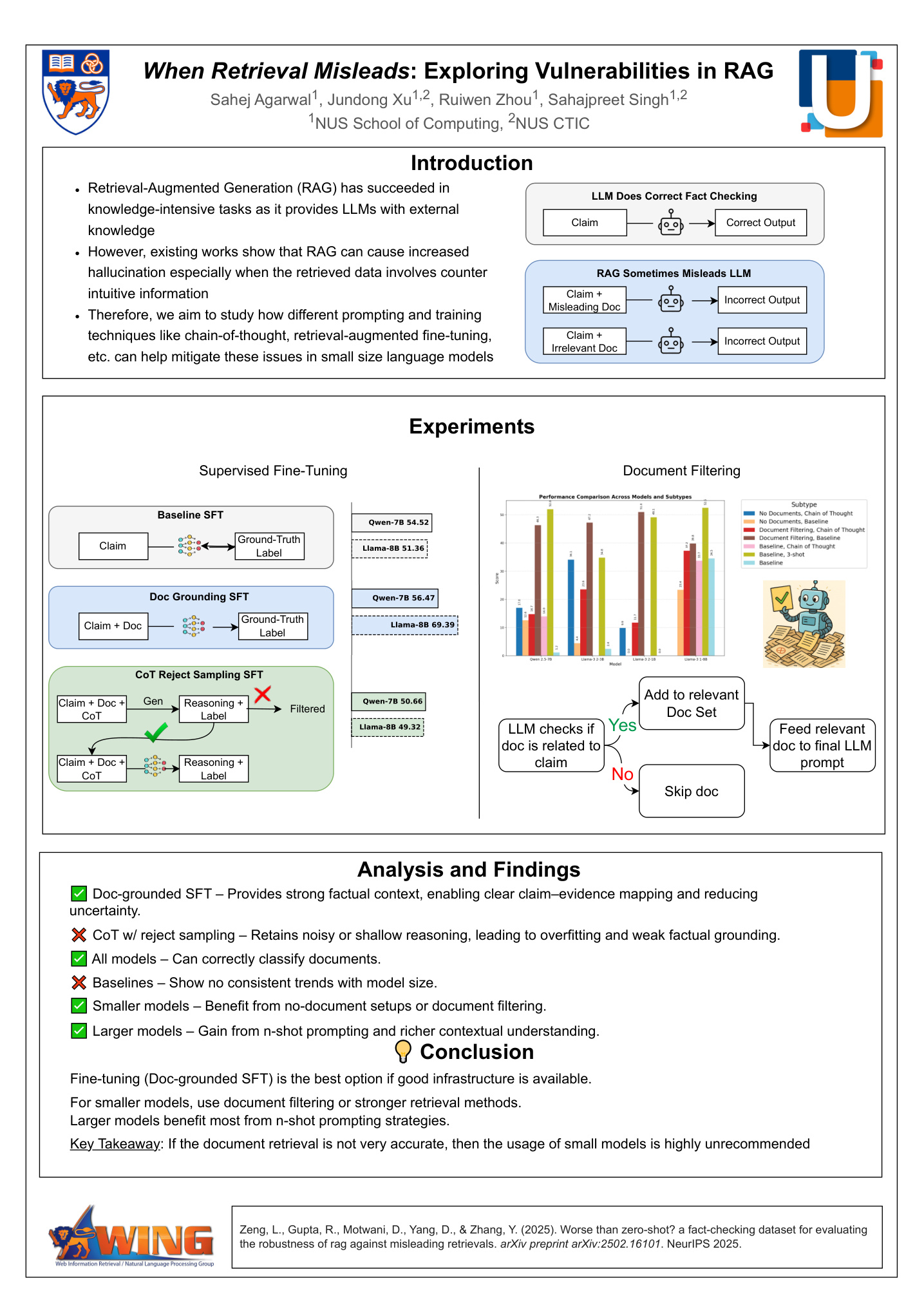 Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Team 11: Contexts Ground Discourse📖 AbstractWe study the impacts of contexts for discourse understanding. ✍️ DescriptionContextual grounding is known to be useful for understanding discourse. However, there is a lack of precise evaluation of its specific benefits. In this project, we systematically study how context can improve the understanding of discourse relations between two arguments in the Wall Street Journal (WSJ) corpus, following the PDTB-style setting. We explore two types of context selection methods: (1) rule-based and (2) similarity-based. Our evaluation metric is our own DiSQ Score. Welcome to our poster session for more details! ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Poster ] | 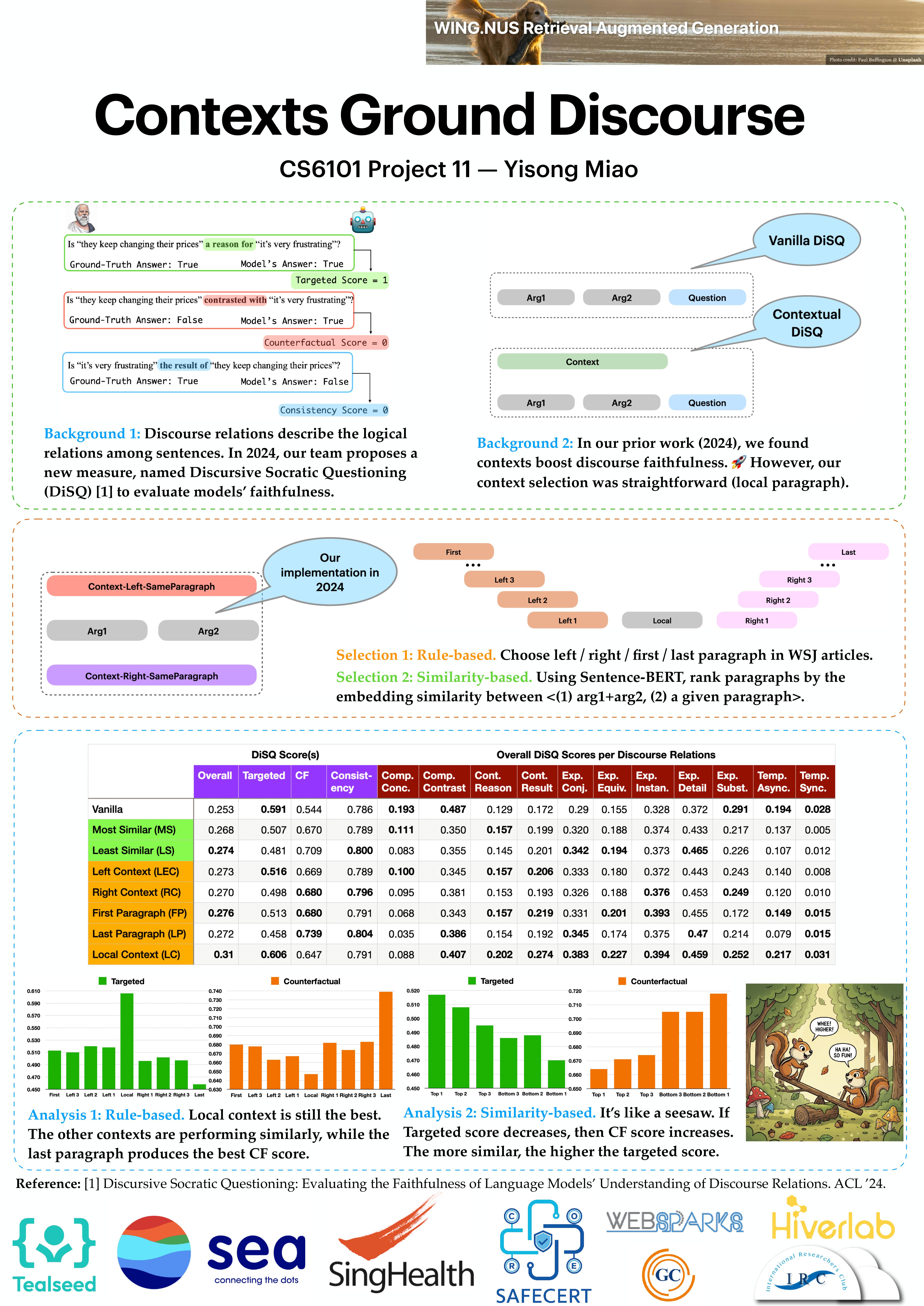 Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Team 12: Context-Aware RAG: Enhancing Retrieval with Contextual Information📖 AbstractTODO ✍️ DescriptionRetrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems augmented with chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning have achieved strong performance on multi-hop question answering, but they incur increased inference latency and produce lengthy contexts that hinder scalability. This project introduces two stopping criteria — a Repetition-aware criterion that detects redundant reasoning tokens and halts generation when steps begin to repeat, and a Confidence-based criterion that terminates reasoning once model's confidence surpasses a threshold. We integrate these criteria into a CoT-enabled RAG pipeline and evaluate their feasibility on HotpotQA and 2WikiMultiHopQA, measuring inference latency, generated-context length, and answer quality. Rather than presupposing benefits, we report our experimental measurements and provide a detailed analysis of the observed advantages and limitations for each method. Our results offer grounded, practical insights into when lightweight stopping mechanisms may help make CoT-RAG systems more efficient and where further refinement is required. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Team 13: Improving Retrieval with Graph Pruning📖 AbstractGraphRAG systems enhance retrieval-augmented generation through knowledge graphs, but scale poorly due to retrieving too much, potentially clouding context due to the lost in the middle problem. We applied a systematic framework as outlined in PathRAG; to efficiently identify and select the most reliable relational path; to the communities relation based approach introduced by Microsoft in their implementation of GraphRAG as introduced in their paper GraphRAG Approach to Query-Focused Summarization. The objective is to retrieve with higher accuracy, reducing computational cost as well as compute time by allowing us to reduce the top K documents that should be retrieved. ✍️ DescriptionGraphRAG systems construct knowledge graphs from document collections to enhance retrieval-augmented generation, but these graphs can become computationally expensive and noisy at scale. Every additional node, edge, and community increases token usage, query latency, and risks introducing irrelevant context that may degrade answer quality. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Team 14: A Unified Benchmark Suite for Retrieval-Augmented Speculative Decoding📖 AbstractRetrieval-augmented speculative decoding has delivered promising gains in prior work, but thus far there has been no effort to make it production-ready. To our knowledge, we are the first to try. ✍️ DescriptionSpeculative decoding (SD) accelerates LLM inference by using a smaller model (drafter) to predict the next few tokens, then using a larger model (verifier) to verify all guesses in parallel. Recent work has explored allowing the drafter to retrieve from vector database as prior, giving rise to retrieval-augmented speculative decoding (RASD). While RASD has yielded promising results, lack of flexible configurability and the existence of multiple diverging techniques make it difficult to apply in practice. We propose a plug-and-play software framework for RASD that (a) allows convenient configuration of all parts of the RASD pipeline including drafter, verifier and vector database, and (b) reports useful metrics for evaluating throughput and generation quality. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Team 16: Beyond the Crowd: LLM-Augmented Community Notes for Governing Health Misinformation📖 AbstractWe uncover major latency in health-related Community Notes and propose CrowdNotes+, an LLM-augmented governance framework combining evidence-grounded note augmentation, utility-guided automation, and hierarchical evaluation. The result: more timely, factual, and effective crowd-sourced health misinformation responses. ✍️ DescriptionCommunity Notes, the crowd-sourced misinformation governance system on X (formerly Twitter), enables users to flag misleading posts, attach contextual notes, and vote on their helpfulness. However, our analysis of 30.8K health-related notes reveals significant latency, with a median delay of 17.6 hours before the first note receives a helpfulness status. To improve responsiveness during real-world misinformation surges, we propose CrowdNotes+, a unified framework that leverages large language models (LLMs) to augment Community Notes for faster and more reliable health misinformation governance. CrowdNotes+ integrates two complementary modes: (1) evidence-grounded note augmentation and (2) utility-guided note automation, along with a hierarchical three-step evaluation that progressively assesses relevance, correctness, and helpfulness. We instantiate the framework through HealthNotes, a benchmark of 1.2K helpfulness-annotated health notes paired with a fine-tuned helpfulness judge. Experiments on fifteen LLMs reveal an overlooked loophole in current helpfulness evaluation, where stylistic fluency is mistaken for factual accuracy, and demonstrate that our hierarchical evaluation and LLM-augmented generation jointly enhance factual precision and evidence utility. These results point toward a hybrid human-AI governance model that improves both the rigor and timeliness of crowd-sourced fact-checking. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Poster ] | 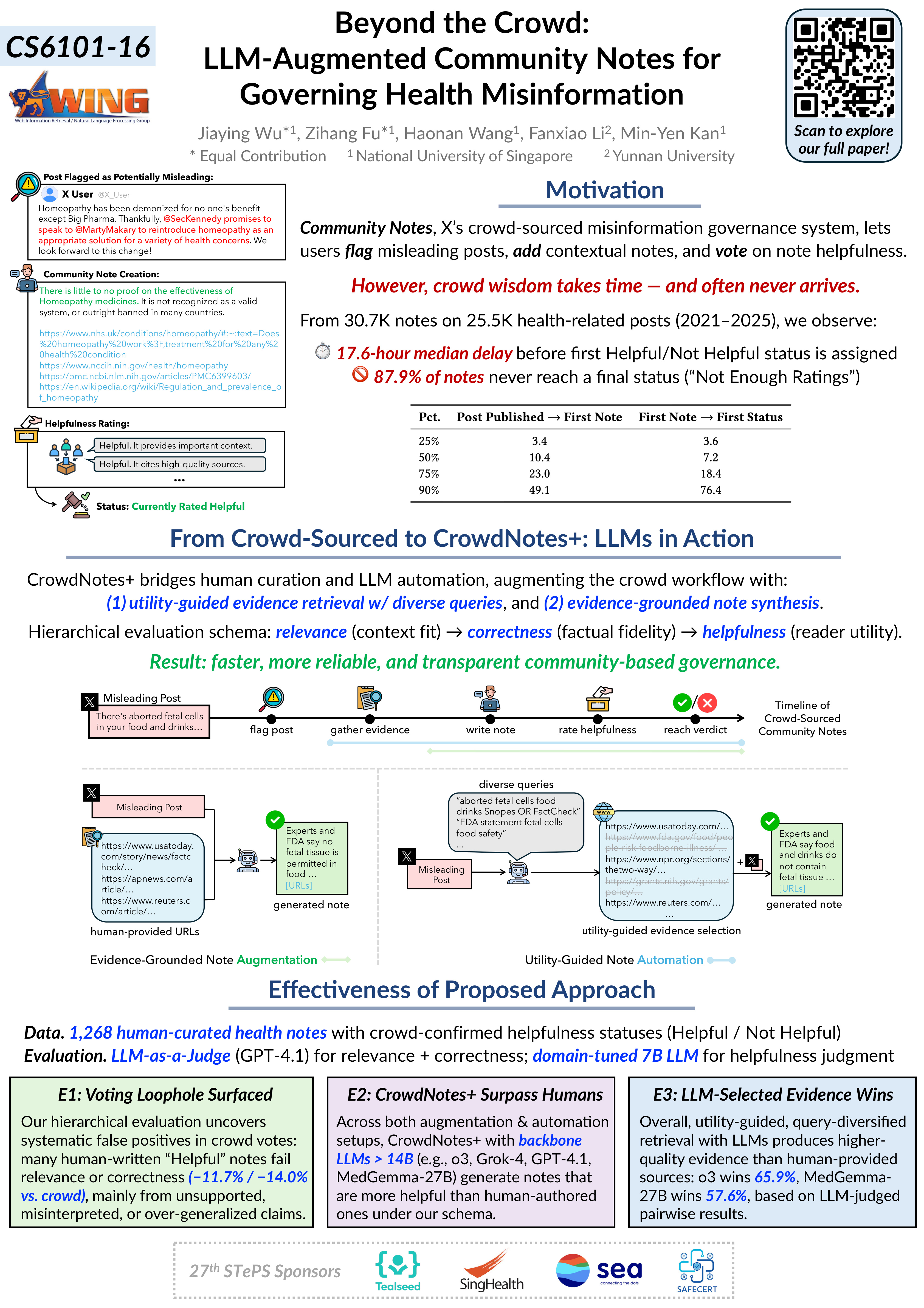 Click the image to enlarge. Click here to view PDF version. |
Projects from Semester 2310 (AY 23/24, Sem I) featured at 23th STePS, held on 15 Nov 2023.
In AY23/24 Sem I, CS6101 was topically oriented on Large Language Models. There were 41 students in 19 teams whose projects focused on recent research on topics related to LLMs.
Projects | Posters |
|---|---|
Team 02: AugICL📖 AbstractAugmented in-context learning for implicit discourse relation classification. ✍️ DescriptionWe present an initial exploration of employing large language models (LLMs) for in-context learning (ICL) in the domain of implicit discourse relations classification. We analyze the effects of several ICL variables on task performance: (1) an inverted U-shaped relationship between the number of demonstrations and performance, (2) minimal impact from sample ordering, and (3) the benefits of incorporating diverse Level 2 sense samples. Additionally, we show that performance of the LLaMA-13B model can match that of the larger ChatGPT (175B) when augmenting with demonstrations akin to test samples. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Poster ] | 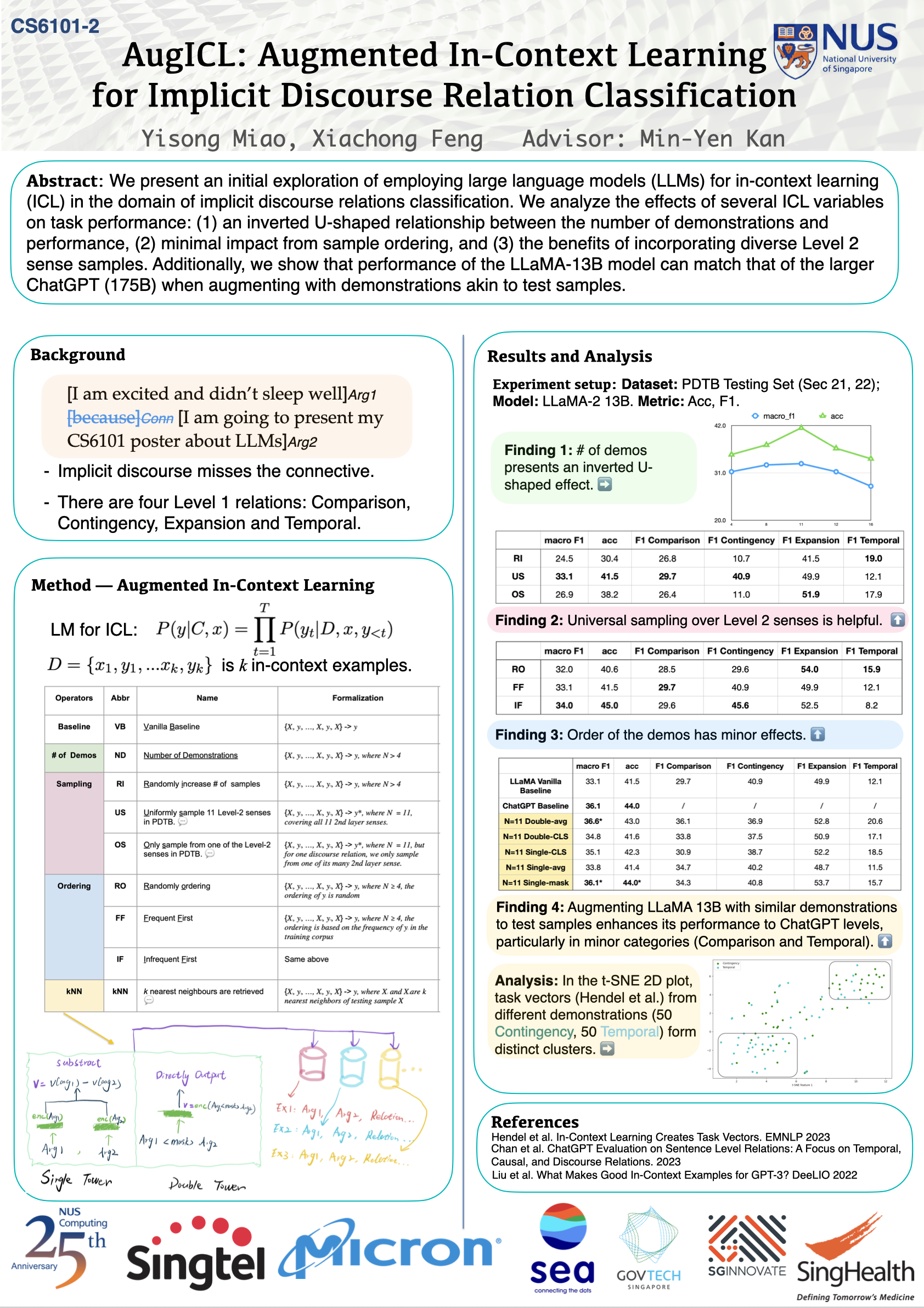 Click the image to enlarge |
Team 05: Chain of Action📖 AbstractChain of Action with agents on code. ✍️ DescriptionIn our work, we leverage advancements in agentic Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance their skill decomposition and autonomous learning capabilities. We introduce a freeform action space, prompting the LLM to decompose complex problems into simpler tasks. Our hypothesis is that this approach will enable the LLM to incrementally build its skill set and strategically chain actions for problem-solving. Furthermore, we propose a novel retrieval-augmented learning framework, encouraging the model to acquire new skills from diverse prompts. This framework aims to enrich the LLM's knowledge base, allowing it to apply newly learned skills to solve the designated problem set effectively. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Project Page ] [ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge |
Team 06: Exploring self-supervised webscraper code generation with LLMs📖 AbstractUsing LLMs to fully self-supervise the creation of a webscraper given a website. ✍️ DescriptionThe process of writing code has been sped-up massively through the rapid adoption of LLMs in the programming process. However, most workflows still largely "human-in-the-loop", with a programmer running, verifying and helping to debug generated programs. We want to test the ability for LLMs to fully self-supervise in the code generation process: verifying if outputs are correct. We test this in the limited context of code generation for website scrapers and achieve a proof-of-concept that LLMs are able to fully self-supervise in the creation of webscrapers, enabling their use as a fully-automated generalized scraping tool. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ GitHub Repository ] [ Poster ] | 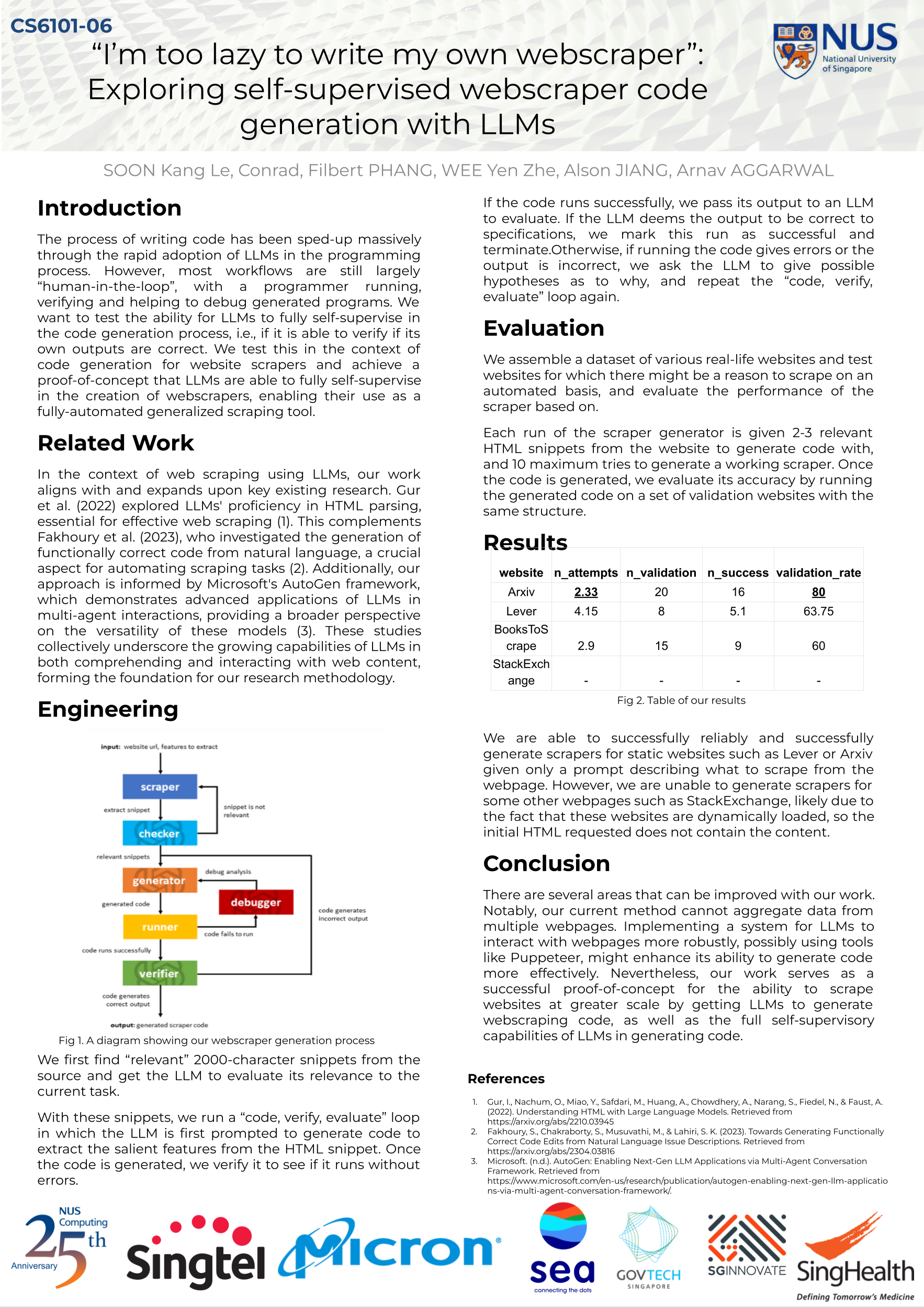 Click the image to enlarge |
Team 09: LLM for Table Fact-Checking & Reasoning📖 AbstractEvaluating the effectiveness of open-source LLM (e.g., LLama2) in table reasoning. ✍️ DescriptionAs tables are a ubiquitous form of data presentation, ensuring their accuracy and reliability is important. This project is motivated by the need for robust table reasoning algorithms. We aim to evaluate the effectiveness of open-source LLM (e.g., LLama2) in this domain. Employing a range of benchmarks, we evaluate the models' accuracy in table reasoning and manually observe the error types. Our results aim to identify the strengths and weaknesses of open-resource LLMs in dealing with structured data, providing insights for future research and application. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ GitHub Repository ] [ Poster ] | 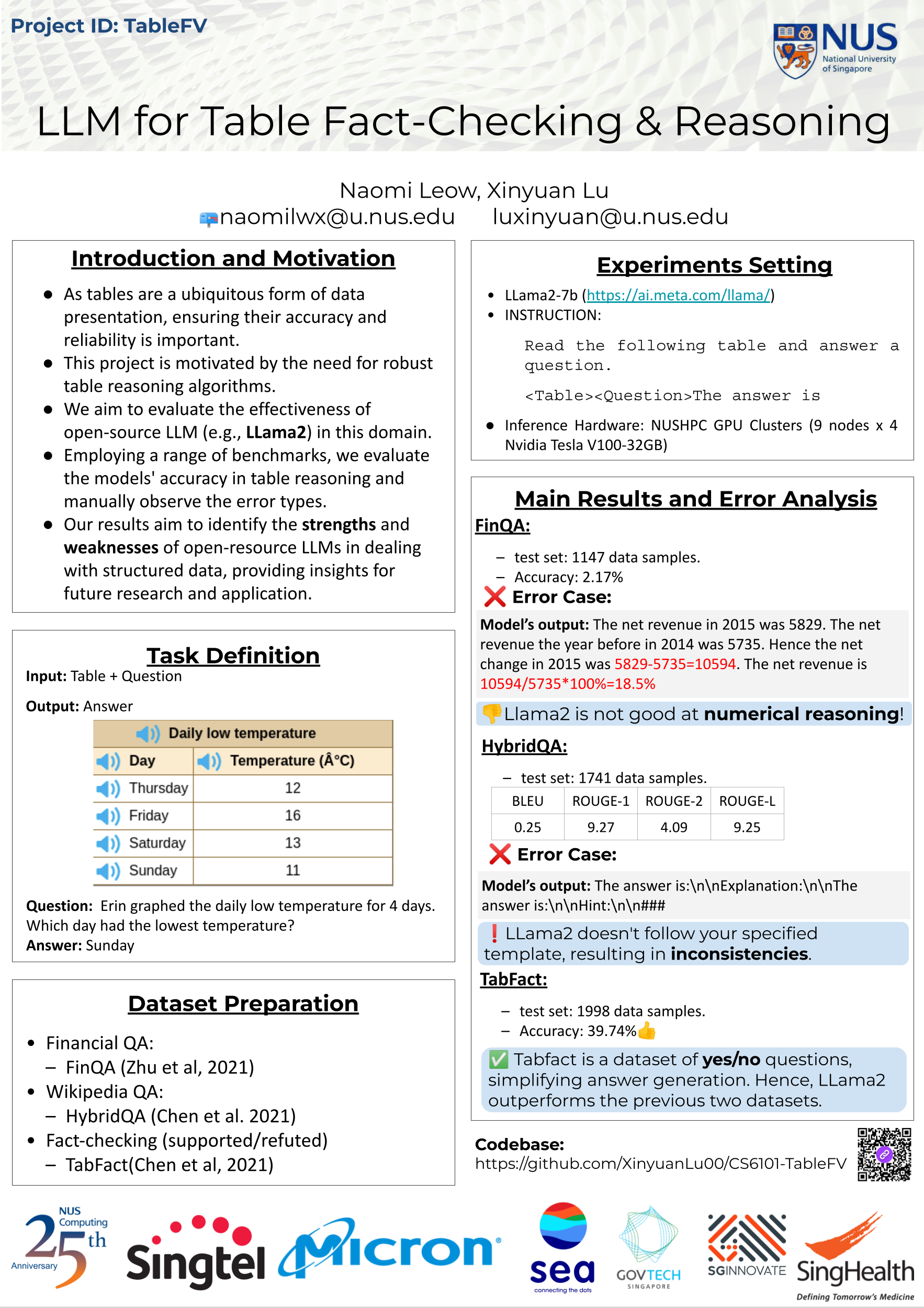 Click the image to enlarge |
Team 14: Textualization of Visual Information📖 AbstractA simple attempt to textualize images via vision experts and evaluate on MMBench. ✍️ DescriptionVisual information (image labels, image captions, object labels, etc.) contains the humans' (or visual model's) understanding and analysis of key features in the image. We investigate the performance of LLMs in directly accomplishing visual perception/reasoning tasks by transforming visual information in images into text via vision experts. We follow LENS framework and evaluate on MMBench and provide some insights. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Project Page ] [ Poster ] | 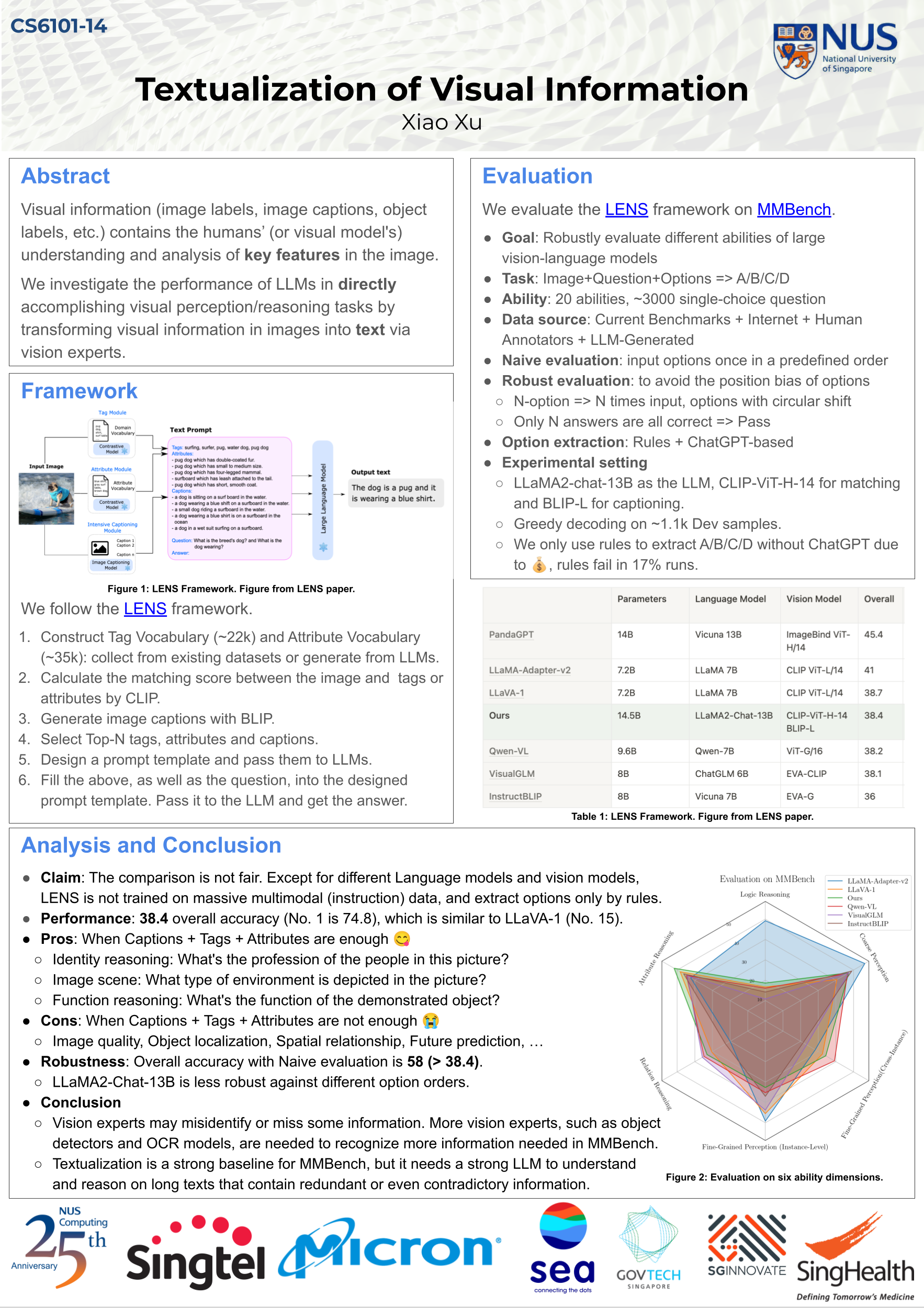 Click the image to enlarge |
Projects from Semester 2020 (AY 20/21, Sem II) featured at 18th STePS, held on 14 Apr 2021.
In AY20/21 Sem II, CS6101 was topically oriented on Conversational Recommendation Systems. There were 26 students in 10 teams whose projects focused on recent research on the topics of Conversational Systems, Recommender Systems and their intersections.
Projects | Posters |
|---|---|
🏆 1st place, Team 07: Extending Neural Collaborative Filtering📖 AbstractExtending the Neural Collaborative Filtering Framework to improve model understanding and robustness. Using additional Convolutional layers, Pairwise Loss Function and Auxiliary Information Embedding to explore potential model improvements. ✍️ DescriptionIn our project, we explore the potential extensions to the Neural Collaborative Filtering (NCF) Framework to improve model understanding and robustness. Using additional Convolutional layers, Pairwise Loss Function and Auxiliary Information Embedding, we experiment with the MovieLens-1M dataset to attain better model performance on Hit Rate and NDCG metrics while attempting to improve model understanding through auxiliary embeddings. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Homepage ] [ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge |
🥈 2nd place, Team 04: Causal Estimation for Conversational Recommender Systems📖 AbstractIn this project, we study popularity bias in Recommender System (RecSys), Conversational Recsys, and their interplays. ✍️ DescriptionWe discover (1) conversation can significantly mitigate popularity bias for traditional RecSys; (2) Conversation RecSys suffers from popularity bias itself. We propose a method to mitigate popularity bias in Conversational RecSys. Please refer to our poster for technical details. Our experiment is still WIP, we will update on this github repo: https://github.com/YisongMiao/cs6101 ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Homepage ] [ Poster ] | 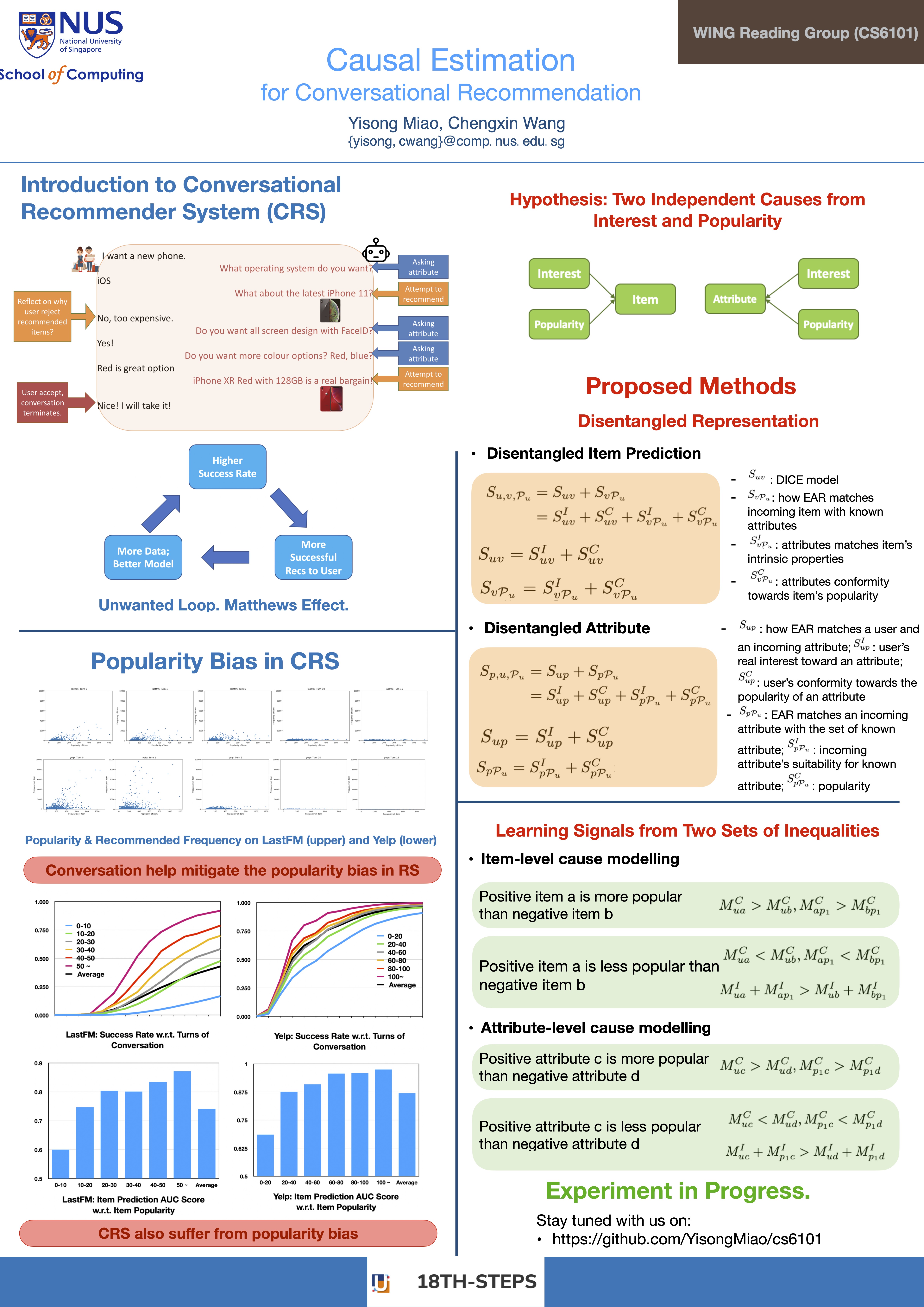 Click the image to enlarge |
🥉 3rd place, Team 09: Beyond IGMC📖 AbstractWe extend the state-of-the-art Inductive Graph Matrix Completion recommender system by introducing Graph Normalization and Layer Aggregation variants, and explore the models' potent transfer learning capabilities. ✍️ DescriptionIn this project, we investigate how recent advances in Graph Neural Network models can impact and even improve the ability of the state-of-the-art Inductive Graph Matrix Completion (IGMC) recommender system to predict ratings in the setting of only having ratings of each user-item interaction. We show this through measuring the baseline model performance against the extensions using the RMSE scoring. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Homepage ] [ Video ] [ Poster ]] |  Click the image to enlarge. |
Team 01: Explore Multiple Response Modalities of DialogWAE📖 AbstractThis project is focusing on assessing and interpreting the GMM prior components in DialogWAE. ✍️ DescriptionNeural response generation is a typical task in NLP community. DialogWAE is a new approach for dialogue modeling and response generation, which achieves SOTA result on popular datasets. In this work, we focus on exploring the various modalities of the generated responses. To be specific, we propose to: • Analyze how the number K of prior components influences the overall performance. • Explore what each prior component of the Gaussian mixture distribution captures when K > 3. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Homepage ] [ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge |
Team 02: FiBiNET📖 AbstractThis project is focusing on combining feature importance and bilinear feature interaction for click-through rate prediction ✍️ DescriptionWe explore potential extensions to one of the state-of-the-art recommender systems named FiBiNET which assigns importance to feature embeddings. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge |
Team 03: Feedback-guided Preference Adaptation Network (FPAN)📖 AbstractMulti-round conversational recommender systems (CRS), which interact with users by asking questions about attributes and recommending items multiple times in one conversation. ✍️ DescriptionFPAN uses gating modules to adapt the user embedding and item-level feedback, according to attribute-level feedback. This project looks to improve the offline and online training of FPAN. It does this by conducting a survey into the effectiveness of GraphSAGE convolutions. And, by introducing a function to calculate user & item bias. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge |
Team 05: Counterfactual Recommender📖 AbstractRelevance Matrix Factorization and Asymmetric Tri-training are employed to build a recommendation system. Its algorithm is evaluated by using Coat dataset to simulate a scenario that we have only biased observational data for model training while evaluating on unbiased data. ✍️ DescriptionImplicit feedback is easy to collect and can be useful to build a recommendation system in online service. However, the feedback suffered from popularity bias because a user gives feedback to an item only if it is exposed. To build an unbiased recommendation system, counterfactual learning and meta learning approaches are applied to deal with such observational data. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge |
Team 06: Diversifying Dialogue Generation with Non-Conversational Text📖 AbstractImplementation for the paper Diversifying Dialogue Generation with Non-Conversational Text on English. ✍️ DescriptionTraditional neural network-based sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) models strongly suffer from the low diversity problem when it comes to open domain dialogue generation. The authors aim to diversify the dialogue generation with non-conversational text corpus in Chinese language. We attempt to extend this work to conversational and non-conversational datasets in English Analysis on how filtering the non-conversational corpus based on topic affects the result (selected topics: Politics, Attitude & Emotion, Health). ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Homepage ] [ Video ] [ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge |
Team 08: NN for Ad Recommendation📖 AbstractThe project extends the popular DeepFM neural network to better predict users' click-through-rate of advertisements. ✍️ DescriptionDeepFM is a popular click-through-rate (CTR) model developed by Huawei's Noah's Ark Lab. In this project, we modifies the original neural network structure for better CTR predictions. More specifically, we introduced pooling layers to better capture the higher order feature interactions and b. added a linear layer to assign weights to the constituent deep model and factorisation machine (FM) model when combining the outputs. Our experimental results show that both extensions are able to improve the accuracy of the original DeepFM model. ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge |
Team 10: KGRecSys📖 AbstractImplementation of the paper "KGAT: Knowledge Graph Attention Network for Recommendation". ✍️ DescriptionIn this project, we implement the KGAT model as described in the paper "KGAT: Knowledge Graph Attention Network for Recommendation". ☀️ Team Member
📻 Media Links[ Homepage ] [ Poster ] |  Click the image to enlarge |
